Ice Cream & Health
Safe to Enjoy Ice Cream During Pregnancy?
Craving something sweet? Learn if you can eat ice cream while pregnant and discover safe, delicious options that satisfy your sweet tooth!

As you embark on the beautiful journey of pregnancy, it’s natural to experience a whirlwind of emotions, cravings, and questions, especially when it comes to food. For many, the thought of indulging in a creamy scoop of ice cream can evoke a sense of nostalgia, comfort, and joy. But amidst the excitement and anticipation, you might wonder, “Can I eat ice cream while pregnant?” Concerns about nutrition, safety, and those pesky cravings can cloud the enjoyment of this delightful treat. The truth is, ice cream can be a source of happiness and a momentary escape from the challenges of pregnancy. Understanding the facts about pregnancy and ice cream can help you navigate this sweet solution with confidence, so you can savor every bite without worry.
Key Takeaways
- Between 50 and 90 percent of pregnant women experience food cravings.
- A pint of premium ice cream may contain over 1,000 calories.
- Pregnant individuals are advised to consume an extra 340-450 calories per day.
- Shop-bought ice cream is generally safe due to pasteurization.
- Be cautious with soft serve ice cream to avoid listeria risks.
- Limit high-sugar ice cream due to potential health effects.
- Avoid flavors with caffeine to stay within daily limits during pregnancy.
Understanding Pregnancy Cravings
Pregnancy can bring about a whirlwind of cravings, which may leave you wondering what’s behind these sudden desires. One of the most common cravings noticed is for ice cream, and this often stems from various physiological changes. Hormonal shifts in your body create the perfect storm for these urges, impacting your taste and appetite.
What Causes Cravings for Ice Cream?
Cravings for ice cream in pregnancy can be attributed to multiple factors. Hormonal fluctuations not only heighten the sense of taste but can also lead to changes in nutritional requirements. Specifically, the body’s need for calcium can be a driving force behind these cravings. Ice cream, being rich in calcium, may subconsciously satisfy this need, encouraging you to indulge in sweet, creamy treats.
Prevalence of Ice Cream Cravings Among Pregnant Women
Pregnancy and ice cream cravings are more common than you might think. Research indicates that between 50% to 90% of pregnant women experience cravings. Ice cream tends to be a favorite among these cravings, highlighting its appeal during this unique time. The cravings generally begin toward the end of the first trimester and peak in the second trimester, with many women noticing a decrease in cravings as they approach the final stages of pregnancy.

| Stage of Pregnancy | Craving Patterns |
|---|---|
| First Trimester | Initial onset of cravings, moderate intensity |
| Second Trimester | Peak cravings, significant desire for sweets like ice cream |
| Third Trimester | Decrease in cravings, often due to fullness |
Can I Eat Ice Cream While Pregnant?
Yes, you can eat ice cream while pregnant, but you should be cautious about your choices. Opt for ice cream made from pasteurized milk to minimize health risks. Pregnant women are more susceptible to listeriosis, a rare but serious infection that can harm both mother and baby. Therefore, being mindful about safe ice cream options during pregnancy is essential.
Soft-serve ice cream can carry listeria if machines are not properly cleaned. Some major fast-food chains use self-pasteurizing machines which can provide a safer choice. If you prefer frozen desserts, consider soft-serve yoghurt as it contains acidity that inhibits listeria growth.
Avoid homemade ice cream unless you’re certain it does not contain raw or undercooked eggs. The nutritional content of ice cream can be quite high; for instance, 100 grams typically contains around 200 calories, 22.86 grams of sugar, and 114 mg of calcium. Keeping portion sizes small can help you enjoy this treat without excessive calorie intake, which is essential during pregnancy.

While enjoying ice cream, always consider the overall diet to prevent complications such as gestational diabetes or high blood pressure. Eating ice cream in moderation, especially when combined with good hygiene practices, can certainly be part of your pregnancy journey. Always consult your healthcare provider for appropriate recommendations tailored to your needs.
Types of Ice Cream: What You Should Know
When it comes to enjoying ice cream during pregnancy, understanding the different types of ice cream available is essential. Each variety has specific safety considerations that can affect your decision. Below, you’ll find key information related to store-bought ice cream, soft serve, and homemade options that can guide you toward safe ice cream options during pregnancy.
Store-Bought Ice Cream Safety
Most commercial ice creams are made from pasteurized milk and eggs, which makes them generally safe for consumption during pregnancy. Popular brands like Häagen-Dazs and Ben & Jerry’s prioritize safety, ensuring their products meet health guidelines. Always read the labels to confirm pasteurization and freshness, as this helps you make informed choices about pregnancy and ice cream.
Soft Serve Ice Cream Considerations
Soft serve ice cream poses unique risks, primarily due to potential contamination from listeria bacteria. Soft-serve machines can harbor this bacteria, particularly if they are not cleaned properly. Expecting mothers should check the hygiene ratings of establishments serving soft serve and consider opting for yogurt-based alternatives, which may present safer options due to the acidity in yogurt that inhibits bacterial growth.
Risks of Homemade Ice Cream
Homemade ice cream often includes raw or undercooked eggs, which can pose a risk of salmonella. Given the heightened sensitivity to foodborne illnesses during pregnancy, it’s advisable to avoid homemade varieties unless you are absolutely sure they do not contain these ingredients. Stick to safe ice cream options during pregnancy that are commercially made to minimize any risks.

Safe Ice Cream Options During Pregnancy
When you have a craving for a sweet treat during pregnancy, choosing the right ice cream is essential. You can still enjoy delicious flavors, but focus on finding safe ice cream options during pregnancy. This ensures both you and your baby stay healthy while satisfying your cravings.
Choosing Pasteurized Ice Cream
Always look for the best ice cream for pregnant women that is made from pasteurized milk. Pasteurization effectively eliminates harmful bacteria, making it a safer choice for expecting mothers. Unpasteurized ice cream can lead to infections, such as listeria, which may have adverse effects on pregnancy. By opting for pasteurized brands, you are prioritizing your health and reducing potential risks.
Flavors to Avoid for Safety
While indulging in ice cream, be cautious of certain flavors with added caffeine, like coffee or green tea varieties. Caffeine intake should be limited during pregnancy, ideally to about 200 milligrams per day. Instead, consider fruit-flavored or classic vanilla varieties, which are generally free of concerns. Always read labels carefully to ensure you are making the safest choices for both you and your baby.
| Ice Cream Flavor | Caffeine Content (mg) | Safe for Pregnancy |
|---|---|---|
| Vanilla | 0 | Yes |
| Chocolate | 0 | Yes |
| Coffee | 30-50 | No |
| Green Tea | 20-30 | No |

Nutritional Value of Ice Cream While Pregnant
Ice cream has a noteworthy nutritional value of ice cream while pregnant, offering certain benefits that can be appealing during this unique time. Primarily, ice cream serves as a source of calcium, which is crucial for fetal development and overall maternal health. In a standard 100-gram serving of ice cream, you can expect to find around 99 to 128 milligrams of calcium. Pregnant women aged 19 to 50 require about 1,000 milligrams of calcium daily, which makes it necessary to include other calcium-rich foods as well.
Beyond calcium, ice cream contains:
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 200-210 |
| Fat | 11g or more |
| Cholesterol | 44mg |
| Carbohydrates | 24g |
| Sugar | 21g |
| Sodium | 80mg |
While the nutritional value of ice cream while pregnant can deliver some benefits, it’s essential to consume it in moderation. High sugar content may lead to weight gain or nutrient deficiencies if overindulged. Additionally, consuming sugary foods like ice cream might increase the risk of gestational diabetes, particularly for women predisposed to this condition.
Consider incorporating other calcium sources into your diet such as cheese, yogurt, and leafy greens to complement the nutritional offerings of ice cream. Be mindful of potential allergic reactions to dairy that could arise during pregnancy.

Health Benefits of Ice Cream During Pregnancy
Ice cream, often considered a guilty pleasure, can actually provide several health benefits of ice cream during pregnancy. Understanding its nutritional profile can help you enjoy this treat while ensuring it fits into your pregnancy diet.
Calcium Content and Other Nutrients
One of the significant advantages of ice cream is its calcium content. Pregnant women require about 1,000 milligrams of calcium daily to support both their health and the development of their baby’s bones and teeth. Ice cream typically contains around 200-210 calories per 100g serving and offers essential nutrients, including fat, carbohydrates, and sugar. Regular consumption of calcium-rich foods is essential, and ice cream can play a part in achieving your calcium objectives while satisfying cravings.
Combining Ice Cream with Healthy Foods
To maximize the health benefits of ice cream during pregnancy, consider combining it with healthier ingredients. Incorporating fruits, nuts, or even yogurt can create a more balanced treat. For example, adding banana slices or berries not only enhances the flavor but also boosts the nutritional value. This approach allows you to enjoy the rich taste of ice cream while maintaining a healthy diet, ultimately supporting your and your baby’s well-being.

Recommendations for Eating Ice Cream in Moderation
Enjoying ice cream can be a delightful experience during your pregnancy, but it is essential to approach it with care. The recommendations for eating ice cream in moderation focus on making conscious choices that allow you to satisfy your cravings while managing your overall health and well-being. When indulging in ice cream during pregnancy, it is important to pay attention to the ingredients and nutritional information. Opt for ice cream options that are lower in added sugars and artificial ingredients. Additionally, always check the ice cream expiration date to ensure that you are consuming a safe and fresh product. By being mindful of these factors, you can enjoy your ice cream treat while prioritizing your health and that of your baby.
Understanding Sugar and Caloric Intake
Most commercial ice creams are high in sugar and calories. A standard serving can contain between 200 to 210 calories, along with 21 grams of sugar, which can contribute to unnecessary weight gain. Since pregnant women require an extra 340 calories a day during the second trimester, it’s crucial to think about where these calories come from. Striking a balance is key to maintaining your health.
- Keep ice cream as an occasional treat, aiming for no more than two or three servings each week.
- Choose lower-sugar options or smaller portions to help manage your caloric intake.
- Read nutritional labels to remain aware of fat content (11 grams or more) and cholesterol levels (44 mg) in your chosen ice cream.
Regular consumption of high-sugar foods can increase the risk of gestational diabetes and other complications. Paying attention to your overall diet will help you make informed decisions that contribute positively to your pregnancy experience. Keep the recommendations for eating ice cream in moderation at the forefront of your choices, and you can treat yourself sensibly.
| Nutrient | Content per 100g Serving |
|---|---|
| Calories | 200 – 210 |
| Fat | 11 g or more |
| Cholesterol | 44 mg |
| Carbohydrates | 24 g |
| Sugar | 21 g |
| Sodium | 80 mg |

Risks and Side Effects of Eating Ice Cream When Pregnant
While you may crave ice cream during pregnancy, it is essential to understand the associated risks of eating ice cream during pregnancy. Moderation is key, as overindulgence can lead to various health issues. One significant concern is weight gain, which may contribute to gestational diabetes. Studies indicate that regular consumption of ice cream is linked to a higher likelihood of developing this condition, particularly in pregnant women.
Excessive ice cream consumption may also increase the risk of developing preeclampsia, a serious condition that can affect both you and your baby. Pregnant women aged between 19 and 50 are advised to maintain a balanced diet to meet nutritional needs, including an intake of 1,000 milligrams of calcium daily. Ice cream, while a source of calcium, contains between 200-210 calories and 11 grams or more of fat per 100g serving.
In some cases, you may experience allergic reactions to dairy or other ingredients in ice cream. High sugar intake from ice cream can also lead to rapid drops in newborn blood sugar levels after delivery, posing risks during the early days of your baby’s life. Furthermore, consuming sugary foods may increase the chances of premature delivery, especially for women who already face preterm risks.
Homemade ice cream carries its own set of dangers. The potential for foodborne illnesses arises when using raw milk or undercooked eggs, as these ingredients can cause serious infections such as Salmonella. The CDC reports significant outbreaks linked to these food products, which can severely impact your health during pregnancy.
It is vital to remain conscious of your ice cream cravings and consumption levels. Here is a brief overview of the potential risks:
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Gestational Diabetes | Regular ice cream intake may increase the risk of this condition. |
| Weight Gain | Excessive calories from ice cream contribute to weight gain during pregnancy. |
| Preeclampsia | Increased sugar and fat intake can elevate risk levels for this condition. |
| Allergic Reactions | Some individuals may face allergies to dairy or other components in ice cream. |
| Premature Delivery | High sugar diets can heighten the risk of early delivery. |

Dealing with Ice Cream Cravings Responsibly
Experiencing cravings for ice cream in pregnancy is not uncommon, especially during the second trimester when these urges often peak. While indulging in your favorite treats can be delightful, it’s essential to manage these cravings responsibly to ensure a balanced and nutritious diet. Listening to your body is important, but so is the moderation of indulgence to maintain your health and that of your baby.
To balance your cravings for ice cream in pregnancy, consider pairing your sweet treats with nutrient-dense meals throughout the day. This approach helps you satisfy those cravings while also ensuring that you receive essential vitamins and minerals necessary for your baby’s development. For example, ice cream could be enjoyed alongside a fruit salad or used in a smoothie with spinach, yogurt, and berries to elevate its nutritional value.
If you find that your cravings become overwhelming or are concerned about your dietary choices, reaching out to a healthcare provider can be beneficial. They can provide tailored strategies for managing cravings for ice cream in pregnancy, guiding you to make choices that suit your nutritional needs without sacrificing the joy of your cravings.
FAQ
Can I eat ice cream while pregnant?
What should I know about cravings for ice cream in pregnancy?
Are there any safe ice cream options during pregnancy?
Is soft serve ice cream safe to eat during pregnancy?
What flavors of ice cream should I avoid during pregnancy?
What is the nutritional value of ice cream while pregnant?
What are the health benefits of ice cream during pregnancy?
How can I manage my ice cream cravings responsibly?
What are the risks of eating ice cream during pregnancy?
Mia is the connector for the “Ice Cream Hater” team, responsible for spreading the word about our brand and building relationships with our audience and partners. With a background in marketing and a passion for community engagement, Mia manages our outreach efforts, coordinates marketing campaigns, and develops strategies to expand our reach. She is passionate about bringing the joy of ice cream to as many people as possible and is always looking for new ways to share our content with the world.
Ice Cream & Health
Does Chocolate Ice Cream Have Caffeine? Find Out Here!
Craving a scoop but concerned about caffeine? Discover whether your favorite chocolate ice cream contains this energizing compound.

Imagine it’s a warm summer afternoon, and you’re on the hunt for a sweet treat to cool down. You reach for a classic bowl of chocolate ice cream, savoring its rich, creamy texture as it melts in your mouth. But then, a thought pops into your mind: does chocolate ice cream have caffeine? For those of us who are mindful of our caffeine consumption, this question holds more weight than you might think. Whether you’re trying to limit your daily intake or simply enjoy that delightful scoop without unexpected jitters, it’s important to get to the bottom of the caffeine content in this beloved dessert. Let’s explore the relationship between chocolate ice cream and caffeine, so you can enjoy your treat with peace of mind.
Key Takeaways
- Chocolate ice cream contains approximately 3 milligrams of caffeine per 100 grams.
- Milk chocolate ice cream has lower caffeine levels compared to dark chocolate varieties.
- A small container of chocolate ice cream (3.5 fluid ounces) provides about 2 milligrams of caffeine.
- Caffeine sensitivity varies among individuals; some may react to even small amounts.
- Understanding caffeine content in different ice cream flavors can aid in making informed dietary choices.
Understanding Caffeine in Foods
Caffeine is a natural stimulant found in a variety of foods and beverages. This compound is well-known for its ability to enhance alertness and energy levels. You might wonder what is caffeine exactly. It’s the component that helps you feel awake and energized, found in items you enjoy daily. Understanding its sources can reveal just how common caffeine really is in your diet.
What is Caffeine?
Caffeine works by blocking adenosine receptors in the brain, which promotes wakefulness. It’s obtained primarily from sources of caffeine such as coffee, tea, and chocolate. Interestingly, chocolate bars and ice creams can also contribute to your overall caffeine intake. Many people consume caffeine through their daily routines without even realizing it, with the average American adult taking in between 120 and 215 milligrams each day.
Sources of Caffeine
There are numerous sources of caffeine that contribute significantly to dietary intake. Here are some common foods and beverages along with their typical caffeine content:
| Food/Beverage | Caffeine Content |
|---|---|
| 8 oz Coffee | 95 mg |
| 12 oz Soft Drink | 34-54 mg |
| 1 oz Dark Chocolate | 23 mg |
| 8 oz Green Tea | 47 mg |
| 1 serving Instant Hot Chocolate | 25 mg |
Soft drinks account for about 16% of caffeine consumption in the U.S., with younger consumers leading the charge. Chocolate, including ice cream, contains varying amounts of caffeine. For example, chocolate ice cream generally has around 3 milligrams of caffeine per 100 grams. Understanding the caffeine in foods you consume can help you manage your daily intake effectively, especially if you’re one of the 85 percent of individuals who consume at least one caffeinated beverage each day.

Does Chocolate Ice Cream Have Caffeine?
When you indulge in chocolate ice cream, you might wonder about its caffeine content. Caffeine levels vary in chocolate products based on the types of chocolate used in their formulation. Understanding these differences can help you identify whether chocolate ice cream contains significant amounts of caffeine.
Chocolate and Caffeine Content
Chocolate contains naturally occurring caffeine, and the caffeine content in chocolate depends greatly on its type. Dark chocolate is known for its higher caffeine levels, providing around 20 mg per ounce. Milk chocolate, on the other hand, typically contains about 6 mg per ounce. When it comes to chocolate ice cream, it generally has much lower caffeine content. Standard chocolate ice cream usually contains approximately 3 to 6 mg of caffeine per 100 grams, placing it considerably lower than dessert options like coffee-flavored ice cream.
Comparing Different Types of Chocolate
Not all chocolate is created equal, and it’s essential to recognize the differences among types of chocolate. Below is a table illustrating the average caffeine content for various types of chocolate:
| Type of Chocolate | Caffeine Content (mg per ounce) |
|---|---|
| Dark Chocolate | 20 |
| Milk Chocolate | 6 |
| White Chocolate | 0 |
While chocolate ice cream does have caffeine, it is significantly less than what you find in coffee ice cream or other caffeinated desserts. Whether you’re enjoying a scoop of chocolate ice cream or opting for other chocolate treats, understanding the caffeine content can help you make informed choices.

The Role of Cocoa in Chocolate Ice Cream
Cocoa plays a vital role in the delicious experience of chocolate ice cream. Understanding the contributions of cacao beans and the associated processing methods aids in grasping how these elements impact the final product.
Cacao Beans and Their Components
Cacao beans are the foundation of chocolate, containing essential components such as fats, sugars, and theobromine. Within these beans, caffeine naturally exists, albeit in lower concentrations compared to other sources. Chocolate ice cream, made from these cacao beans, integrates flavors and unique characteristics. For example, it generally contains 3 mg of caffeine and 62 mg of theobromine per 100 grams. The transformation of cacao beans into chocolate and subsequently into ice cream reflects a process rich in flavor development and depth.
Impact of Cocoa Processing on Caffeine Levels
The cocoa processing methods significantly influence the caffeine levels in chocolate, particularly in ice cream. As chocolate undergoes various stages of processing, the concentration of caffeine often decreases. In products where dairy and sugar are predominant, such as chocolate ice cream, the caffeine levels can be notably lower than in the raw cacao beans. For instance, milk chocolate varieties usually contain less cocoa solids than dark chocolate, resulting in reduced caffeine levels. Understanding these transformations helps you appreciate the complexity of chocolate ice cream and the subtleties of its flavor profile.
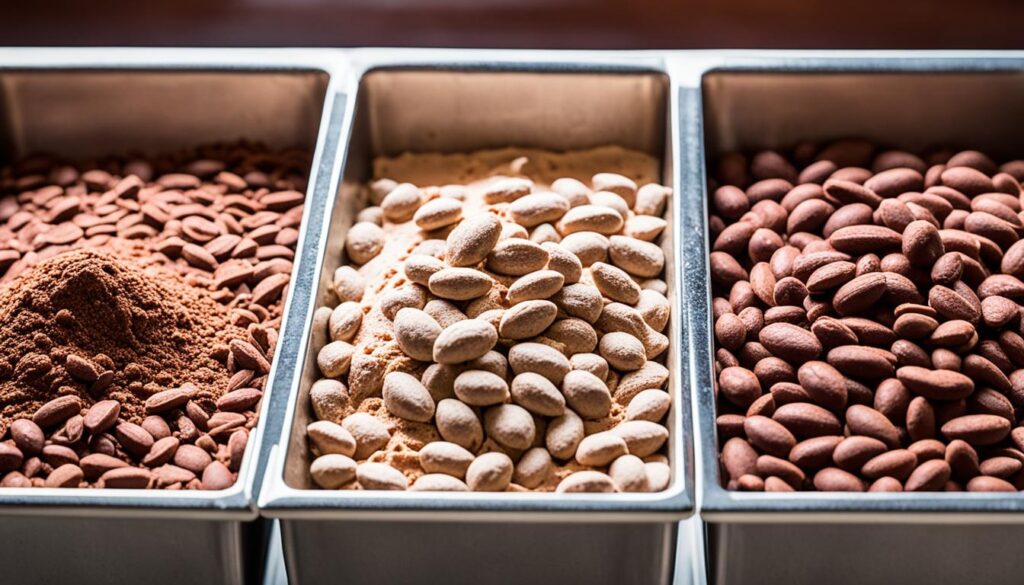

| Chocolate Type | Caffeine Content (mg/100g) | Theobromine Content (mg/100g) |
|---|---|---|
| Chocolate Ice Cream | 3 | 62 |
| Milk Chocolate | 10-20 | 80-150 |
| Dark Chocolate | 30-60 | 150-200 |
Different Types of Chocolate Ice Cream
When it comes to chocolate ice cream, you have several delightful options to choose from. Understanding each type can enhance your enjoyment, especially if you’re mindful of caffeine content.
Milk Chocolate Ice Cream
Milk chocolate ice cream typically boasts a creamy, rich flavor profile. With a lower caffeine content, averaging about 3 mg per 100 grams, it provides a more mellow chocolate experience. This creamy treat is perfect for those who prefer a subtle hint of chocolate without the heightened caffeine levels found in darker varieties.
Dark Chocolate Ice Cream
In contrast, dark chocolate ice cream offers a bolder flavor and denser texture. This type has a higher caffeine content, around 5 mg per 100 grams. The intense cocoa flavor makes it a favorite for chocolate aficionados looking for an indulgent and slightly bitter taste. The increased caffeine can provide an energizing boost that some enjoy.
Chocolate Flavored Ice Cream vs. Chocolate Ice Cream
Not all chocolate-flavored ice cream is created equal. Chocolate flavored ice cream may contain little to no actual chocolate, which typically results in lower caffeine content compared to both milk chocolate and dark chocolate ice cream. If you’re looking for a sweeter treat without the chocolate intensity, this option might be your best bet.

Caffeine in Other Chocolate Desserts
When indulging in chocolate desserts, it’s essential to recognize that caffeine can be present in various forms. Beyond chocolate ice cream, other sweet treats may surprise you with their caffeine content. Let’s explore how different desserts stack up in terms of caffeine levels.
Caffeine Levels in Chocolate Cake and Pudding
Chocolate cake is a favorite dessert for many. On average, chocolate cake contains approximately 6 mg of caffeine per serving. This is primarily due to the cocoa used in the recipe. For a delightful alternative, chocolate pudding includes about 2 mg of caffeine per serving, making it a lower-caffeine option for those who want to enjoy a creamy dessert without too much stimulation.
Caffeine in Ice Cream Flavors with Coffee
If you are a fan of coffee-flavored desserts, be prepared for an increase in caffeine content. Many ice cream flavors incorporate coffee, significantly raising the caffeine levels. For instance, certain premium brands offer coffee ice cream with caffeine content reaching 35 mg per serving. Combining chocolate and coffee, such as in coffee chocolate ice cream, can elevate your experience while also increasing your caffeine intake. Popular coffee dessert options like frappes or coffee-infused ice creams seamlessly blend your love for chocolate and caffeine.

| Dessert Type | Caffeine Content (mg per serving) |
|---|---|
| Chocolate Cake | 6 |
| Chocolate Pudding | 2 |
| Coffee Chocolate Ice Cream | 35 |
Understanding the caffeine in desserts allows you to make informed choices, whether you prefer the moderate chocolate cake caffeine or the more robust coffee ice cream caffeine. Enjoy your delightful treats responsibly as you savor the rich flavors!
Health Implications of Caffeine Consumption
Caffeine consumption plays a significant role in many people’s daily routines. Understanding the health implications can help you make informed choices about your daily caffeine intake. Different populations react uniquely to caffeine, highlighting the necessity for tailored recommendations.
Recommended Daily Caffeine Intake
In the United States, more than 90 percent of adults regularly consume caffeine, averaging over 200 milligrams per day. The FDA indicates that a maximum daily caffeine intake of 400 milligrams is safe for most healthy adults. Here’s a quick breakdown of caffeine content in some common beverages:
| Beverage | Caffeine Content (mg) |
|---|---|
| 8-ounce cup of coffee | 95-200 |
| 12-ounce can of cola | 35-45 |
| 8-ounce energy drink | 70-150 |
| 8-ounce cup of tea | 14-60 |
Those in vulnerable groups, such as pregnant women, should limit their caffeine intake to under 200 milligrams to avoid potential risks. High caffeine levels can lead to various health effects of caffeine, particularly during pregnancy, where consumption above 300 milligrams may result in complications.
Effects of Caffeine on Different Populations
Research shows caffeine can lower the risk of certain diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Regular coffee consumption may even decrease the risk of cirrhosis and slow disease progression in hepatitis C. Women who drink coffee may experience a lower risk of stroke compared to those who consume less. Yet, excessive caffeine intake can lead to adverse health effects, particularly among children and older adults, who should monitor their health effects of caffeine more closely.
Caution is essential when consuming energy drinks, which have been linked to significant adverse health effects. The rising consumption of these products has coincided with a substantial increase in emergency room visits for related complications. Understanding these nuances around daily caffeine intake will empower you to make safer choices regarding your beverage consumption.

Does Chocolate Ice Cream Make You Jittery?
When indulging in a scoop of chocolate ice cream, you might wonder if it will leave you feeling jittery. Understanding caffeine sensitivity is key to addressing this query. Caffeine, although present in lower amounts in chocolate products, can still cause various responses in individuals. If you’re someone who experiences the jittery effects of caffeine easily, moderation is essential.
Understanding Sensitivity to Caffeine
Caffeine sensitivity varies significantly between individuals. For some, even small quantities can lead to feelings of nervousness and agitation. Those who are particularly sensitive to caffeine may find that sugary treats like chocolate ice cream provoke unwanted reactions. If you identify as caffeine sensitive, it’s wise to monitor your consumption closely. Be aware of the ingredients in your ice cream, as even trace amounts of caffeine can make you feel jittery.
Factors That Influence Caffeine’s Effects
Several factors can impact how your body reacts to caffeine, including:
- Genetics: Your genetic makeup can dictate how your body metabolizes caffeine, affecting sensitivity levels.
- Consumption Habits: Regular caffeine intake can build tolerance, while infrequent indulgence may heighten sensitivity.
- Overall Health: Physical health conditions and medications may influence your response to caffeine.
Chocolate ice cream contains only negligible caffeine, but if you’re highly sensitive, even this small amount could trigger unwanted symptoms. Enjoying treats mindfully helps maintain a balance between savoring your favorites and managing caffeine-related jitters.

| Factor | Impact on Caffeine Sensitivity |
|---|---|
| Genetics | Affects how caffeine is metabolized and tolerated. |
| Consumption Habits | Regular use can lead to increased tolerance. |
| Overall Health | Certain conditions may exacerbate sensitivity and reactions. |
Alternatives to Chocolate Ice Cream
If you’re searching for delicious low-caffeine desserts or no-caffeine options, there are a variety of alternatives to chocolate ice cream that can satisfy your sweet tooth. These alternatives not only cater to those who are sensitive to caffeine but also offer a delightful range of flavors and textures.
Low-Caffeine and No-Caffeine Options
When avoiding caffeine, sorbets and fruit-based frozen desserts are top choices as they typically contain no caffeine whatsoever. Vanilla ice cream, made from rich creamy dairy, presents a fantastic dessert choice, often containing minimal to no caffeine. If you want something with a bit of flavor, consider yogurt-based options that can be sweetened naturally with fruits or honey.
Other Dessert Choices Without Caffeine
In addition to frozen treats, consider dessert bars and snacks that specifically advertise as caffeine-free. These options can provide the indulgent flavors you crave without the unwanted caffeine kick. You might also explore baked goods like sponge cakes or oatmeal cookies, which can be made without coffee or chocolate, ensuring a delightful and safe sweet treat.

Conclusion
In conclusion, while you may wonder does chocolate ice cream have caffeine, the reality is that the levels are relatively low compared to other popular sources such as coffee or energy drinks. A typical serving of chocolate ice cream contains a modest amount of caffeine derived from the chocolate used in its formulation. For example, dark chocolate ice cream can have more caffeine than its milk chocolate counterpart; however, none of these amounts typically surpass what you’d find in a cup of coffee or an espresso shot.
Understanding the caffeine content can enhance your caffeine awareness, empowering you to enjoy chocolate ice cream as a delightful treat. The chocolate ice cream benefits extend beyond its taste, providing a fulfilling dessert that’s satisfying while allowing you to keep your caffeine intake within healthy limits. Remember, moderation is key, and being mindful of your personal sensitivity to caffeine will help you enjoy your favorite flavors without adverse effects.
Ultimately, the enjoyment of chocolate ice cream can fit seamlessly into your lifestyle, whether you indulge occasionally or make it a part of your regular dessert rotation. Just keep in mind the caffeine levels and have fun discovering the various chocolate ice cream options available, ensuring that your sweet cravings are met in a balanced way.
FAQ
Does chocolate ice cream have caffeine?
How does the caffeine content in chocolate ice cream compare to coffee ice cream?
What factors affect the caffeine levels in chocolate ice cream?
Can eating chocolate ice cream make me feel jittery?
Are there chocolate ice cream options that are caffeine-free?
How much caffeine is in other chocolate desserts, like chocolate cake or pudding?
What should I consider regarding my daily caffeine intake?
What are some other dessert choices without caffeine?
Mia is the connector for the “Ice Cream Hater” team, responsible for spreading the word about our brand and building relationships with our audience and partners. With a background in marketing and a passion for community engagement, Mia manages our outreach efforts, coordinates marketing campaigns, and develops strategies to expand our reach. She is passionate about bringing the joy of ice cream to as many people as possible and is always looking for new ways to share our content with the world.
Ice Cream & Health
Why Does Ice Cream Make Me Cough?
Wondering why ice cream triggers your cough? Discover the surprising reasons behind this discomfort and how to find relief.

Ice cream can make you cough because its cold temperature irritates your throat and respiratory tract. If you're sensitive, this irritation can trigger your cough reflex. Plus, dairy proteins might increase mucus production, leading to more coughing. The high sugar content can worsen throat irritation and even promote infections. If you have GERD, the fat in ice cream could relax your esophagus and cause further throat discomfort. Staying hydrated and consuming warm drinks afterward can help, but there's more to uncover about preventing these annoying coughs.
Key Takeaways
- The cold temperature of ice cream can irritate the throat and respiratory tract, triggering a cough reflex in sensitive individuals.
- Dairy proteins may increase mucus production, leading to throat irritation and subsequent coughing.
- High sugar content in ice cream can worsen throat infections, causing further irritation and coughing.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause throat irritation and coughing after consuming ice cream due to acid reflux.
- Staying hydrated and consuming warm liquids after eating ice cream can help soothe throat irritation and reduce coughing.
Reasons Ice Cream Causes Coughing
When you indulge in a scoop of ice cream, you mightn't realize it could trigger a cough. The cold temperature of ice cream can irritate your throat and respiratory tract, potentially activating your cough reflex.
If you have asthma or respiratory sensitivities, that chilly treat can even induce bronchospasm, leading to more coughing as your body struggles to breathe comfortably. Additionally, maintaining good indoor air quality with tools like air purifiers can help reduce respiratory irritants, especially for those sensitive to allergens or pollutants air purifiers reduce allergens.
Dairy plays a significant role here too. The proteins found in ice cream can cause allergic reactions or enhance mucus production, which can lead to unwanted respiratory symptoms.
As your body produces more mucus to clear the airway, you might find yourself coughing more frequently.
Additionally, the high sugar content in ice cream can promote throat infections, exacerbating irritation and making you more prone to coughing.
If you're already sensitive to dairy, this thickening of mucus can be particularly troublesome, as it creates blockages that your body desperately tries to clear.
Allergy Considerations

Allergies can complicate your enjoyment of ice cream, especially for those sensitive to dairy. Dairy proteins found in ice cream are common allergens that can trigger respiratory symptoms like coughing, sneezing, and throat irritation. If you have a dairy allergy, it's vital to be aware of the potential for an allergic reaction, which can sometimes escalate to anaphylaxis.
Additionally, understanding your personal risk factors for breast cancer can help you make informed dietary choices. Consulting an allergist can help you manage these risks effectively.
Additionally, ice creams containing sulfites—often used as preservatives—can exacerbate coughing, particularly if you have asthma symptoms. Reading ingredient labels is essential to identify potential allergens. Many ice cream products may hide dairy components or other triggers that could cause a reaction.
If you're lactose intolerant or have a dairy allergy, consider opting for dairy-free alternatives like almond or coconut milk ice creams. These options can help you enjoy a frozen treat without the risk of coughing or other allergic reactions.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease

If you've ever experienced a persistent cough or heartburn after enjoying ice cream, you might be dealing with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This condition occurs when stomach acid flows back into your esophagus, often triggered by high-fat foods like ice cream.
Understanding financial responsibilities towards step-children can also be essential in managing life changes associated with divorce.
Managing your dietary choices can help reduce these uncomfortable symptoms and improve your overall respiratory health.
GERD Symptoms Overview
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) can disrupt your daily life with uncomfortable symptoms like heartburn, coughing, and throat irritation. When you experience GERD, stomach acid flows back into your esophagus, leading to these distressing symptoms.
You might notice that certain foods, including ice cream, can trigger or worsen your reflux. The high-fat content in ice cream can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing acid to escape and causing that annoying cough or throat irritation.
Common GERD symptoms include not just heartburn and cough, but also a sour taste in your mouth and difficulty swallowing. If you're frequently dealing with these issues, it's important to recognize them as signs of GERD.
The persistent reflux can lead to further complications, like esophagitis or strictures, which makes it vital to seek medical advice.
Managing GERD symptoms often involves lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding heavy meals before bed.
It's also common to use over-the-counter medications like antacids or proton pump inhibitors to help reduce stomach acid and alleviate symptoms. Understanding your triggers can greatly improve your quality of life.
Dietary Management Strategies
Managing your diet is a key part of controlling GERD symptoms. When you enjoy ice cream, it might trigger Gastroesophageal reflux, leading to persistent coughing or even an asthma attack.
To help minimize these reactions, consider the following dietary management strategies:
- Opt for vanilla or strawberry flavors instead of mint or chocolate.
- Eat smaller portions of ice cream rather than large servings.
- Wait at least two to three hours before lying down after eating.
- Incorporate more frequent meals throughout the day to avoid overloading your stomach.
- Consult a healthcare professional about potential treatments like proton pump inhibitors.
Mucus Production and Throat Issues
When you enjoy cold treats like ice cream, you might notice an increase in mucus production and throat irritation.
This thickened mucus can trigger coughing as your body tries to clear your airways.
Staying hydrated and opting for warm liquids can help ease these symptoms and counteract the effects of cold foods.
Cold Foods Effect
Cold foods like ice cream can have a surprising impact on your throat and respiratory system. When you indulge in that frosty treat, you might experience throat irritation, leading to coughing. This reaction occurs because the cold temperature can trigger bronchospasm in sensitive individuals, constricting the airways.
Additionally, ice cream, being a dairy product, can ramp up mucus production, making matters worse.
Here's what might happen when you dig into cold foods:
- A sudden chill hits your throat, causing discomfort
- Your airways constrict, leading to a coughing fit
- Mucus thickens, creating an obstacle in your respiratory system
- Your body reflexively coughs to clear the obstruction
- You find yourself reaching for a warm drink to soothe your throat
As you enjoy your ice cream, remember that the combination of cold temperatures and increased mucus can cause coughing. Staying hydrated while consuming cold foods can help ease throat irritation and keep mucus in check, allowing you to enjoy your treat with fewer consequences.
Mucus Thickness Connection
Although ice cream can be a delightful treat, it often leads to increased mucus production and thickness, which can create throat issues. When you enjoy that creamy scoop, the dairy content may irritate your respiratory tract, triggering a cough. This reaction is particularly noticeable if you're already experiencing respiratory symptoms.
Cold foods like ice cream can also thicken mucus, prompting your body to cough as a reflex to clear any airway blockages. If you notice thickened mucus after indulging in ice cream, it could signal irritation from both the cold temperature and the dairy proteins. Clear mucus usually indicates allergies, while the thickness you experience might suggest a different issue.
For those with respiratory infections, consuming ice cream can worsen symptoms, leading to even more frequent coughing. To combat mucus thickness and alleviate throat discomfort, you should prioritize hydration. Staying well-hydrated can help thin the mucus, making it easier to clear your airways.
Hydration Importance
After enjoying ice cream, staying hydrated is essential for managing mucus production and throat issues. Without sufficient hydration, mucus can thicken, leading to increased throat irritation and persistent coughing, especially after consuming cold foods.
Here are some hydration tips to keep in mind:
- Sip on warm herbal teas for soothing comfort.
- Enjoy broths that warm you up and hydrate your body.
- Opt for water infused with fruits for a rejuvenating twist.
- Inhale steam from a hot shower to loosen mucus.
- Keep a humidifier running to maintain moisture in the air.
Adequate hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining overall lung health, particularly for those dealing with asthma or other respiratory issues.
When your throat feels irritated after indulging in cold treats, remember that drinking warm liquids can alleviate discomfort and support mucus management. Staying hydrated helps thin mucus, making it easier for your body to clear your airways.
Swallowing Difficulties and Dysphagia

Many people underestimate how common swallowing difficulties, known as dysphagia, can be, especially among older adults or those with certain medical conditions. When you eat ice cream, its texture and temperature can make it harder to manage in your throat, potentially triggering a coughing reflex as your body tries to clear the airway.
For individuals with dysphagia, the sensation of food being stuck or even pain while swallowing can lead to serious choking hazards. To help you better understand the impact of dysphagia, here's a quick reference table:
| Symptoms of Dysphagia | Risks Involved | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Difficulty swallowing | Choking on food or liquids | Sit upright while eating |
| Coughing after eating | Aspiration into the lungs | Opt for thickened foods |
| Feeling of food stuck | Malnutrition or dehydration | Seek a medical evaluation if persistent |
| Pain while swallowing | Social isolation | Consult a speech therapist for exercises |
If you experience persistent swallowing difficulties, it's essential to seek a medical evaluation to guarantee proper management and dietary adjustments tailored to your needs.
Remedies and Expert Recommendations

When it comes to enjoying ice cream without the nagging cough that can follow, several remedies and expert recommendations can assist. By taking proactive steps, you can mitigate the discomfort and fully savor your treat.
- Drink plenty of fluids: Warm herbal teas, like turmeric or honey-infused varieties, can soothe your throat and help reduce coughing.
- Stay hydrated: Consuming warm liquids while enjoying ice cream can counteract potential throat irritation and mucus production.
- Use a humidifier: In dry environments, this can maintain moisture in the air, alleviating throat irritation.
- Inhale steam: Utilizing steam or eucalyptus oil can enhance respiratory comfort and clear mucus.
- Consult a healthcare provider: Especially if you have asthma or dairy sensitivities, personalized dietary recommendations can guarantee safe ice cream consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Do I Always Cough After Eating Ice Cream?
You might cough after eating ice cream because its cold temperature irritates your throat. Additionally, if you're sensitive to dairy or have GERD, the combination could trigger coughing as your body reacts to these irritants.
Why Does Cold Dairy Make Me Cough?
Cold dairy hits your throat like a winter wind, triggering irritation. It can cause mucus thickening and even bronchospasm, especially if you have sensitivities. Monitor your reactions, and consider avoiding it when you're feeling unwell.
Why Does Ice Cream Make My Throat Scratchy?
When you eat ice cream, the cold temperature can irritate your throat, causing a scratchy feeling. Additionally, its dairy content might trigger sensitivities, and the high sugar can lead to further throat discomfort.
Why Do I Cough up Phlegm After I Eat?
When you eat, your body's on high alert, often producing extra mucus. This excess can trigger coughing, especially if you're sensitive to certain foods or temperatures, leading to that annoying phlegm buildup you experience.
Conclusion
Next time you enjoy a scoop of ice cream, remember it's not just a treat; it can be a trigger for your throat's sensitivity. Like a sudden chill in the air, that cough can remind you of hidden issues waiting to be addressed. Whether it's allergies or reflux, listening to your body is key. So, savor each bite with awareness, turning a moment of sweetness into a chance for understanding and care for your health.
Giulia is the creative force behind our content strategy. With a knack for storytelling and a deep understanding of what our readers want, she plans and develops the content that keeps “Icecream Hater” fresh and exciting. Giulia works closely with the editorial team to ensure that every article, recipe, and review aligns with our mission and vision. She aims to inspire our readers to explore, create, and enjoy ice cream in new and innovative ways.
Ice Cream & Health
Is Frozen Yogurt Healthier Than Ice Cream?
Knowing the differences in calories and health benefits, could frozen yogurt truly be the healthier dessert option? Discover the surprising facts!

Frozen yogurt is often the healthier choice compared to ice cream. It typically contains fewer calories, about 114 calories per half-cup, versus ice cream's 140 calories. You'll also find frozen yogurt has less fat, with around 2.5 grams compared to ice cream's 4.5 grams. Additionally, frozen yogurt may offer probiotics that support digestive health, while ice cream usually lacks these benefits. However, watch out for added sugars in frozen yogurt, which can counteract its healthiness. Exploring more about serving sizes and toppings can help you make better choices in satisfying your sweet tooth.
Key Takeaways
- Frozen yogurt generally has lower calories and fat content compared to ice cream, making it a lighter option.
- Frozen yogurt may contain probiotics, promoting digestive health, while ice cream typically lacks these benefits.
- The sugar content in frozen yogurt can be higher due to added sugars for flavor enhancement.
- Portion control is crucial, as both frozen yogurt and ice cream can lead to significant calorie intake, especially with toppings.
- Homemade frozen yogurt allows for healthier ingredient choices and better control over added sugars compared to commercial products.
Nutritional Comparison
When comparing frozen yogurt and ice cream, it's clear that each has its own nutritional profile worth considering.
You'll notice that frozen yogurt typically has fewer calories, averaging around 114 calories per 1/2 cup, while ice cream clocks in at about 140 calories for the same serving size. If you're watching your fat content, frozen yogurt is often the healthier option, containing around 2.5g of total fat compared to ice cream's 4.5g.
Additionally, frozen yogurt can be a source of probiotics, which may aid in digestive health, similar to how certain teas like rooibos tea benefits may promote gut health.
However, don't overlook the sugar content. While they can be similar, frozen yogurt might have more added sugars to boost flavor, which can sometimes push its sugar levels higher than those found in ice cream.
On the plus side, both treat options provide comparable calcium content, essential for your bone health, with frozen yogurt offering about 143mg per serving and ice cream about 128mg.
Ingredients and Production

Frozen yogurt and ice cream differ markedly in their ingredients and production methods, impacting their taste and health profiles. Understanding these differences can help you make informed choices.
| Aspect | Frozen Yogurt | Ice Cream |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredients | Yogurt or cultured milk | Cream |
| Fat Content | 2-6% milk fat | At least 10% milk fat |
| Production Process | Fermentation with yogurt cultures | Churned to incorporate air |
Frozen yogurt typically has a lower fat content due to its yogurt base, while ice cream's cream base results in richer flavors. The fermentation process in frozen yogurt gives it a tangy taste, while the churning method in ice cream creates a lighter, fluffier texture.
Both options can contain added sugars; however, frozen yogurt often has higher levels to balance its tartness. It's essential to check labels for specific nutritional information, as ingredient variations can greatly influence healthiness. Ultimately, knowing what goes into your treat can guide you toward better choices for your diet.
Health Benefits of Each

Choosing between frozen yogurt and ice cream can considerably impact your health, especially if you're mindful of calories and fat intake. Frozen yogurt typically contains fewer calories—about 114 calories per 1/2 cup—compared to ice cream, which has approximately 140 calories per the same serving. This makes frozen yogurt a lighter option for those watching their calorie consumption.
Additionally, many frozen yogurt varieties are made with specialty ingredients that can enhance flavor and health benefits, similar to how specialty beans can elevate coffee experiences.
Furthermore, the lower fat content in frozen yogurt, ranging from 3% to 6% milk fat, is beneficial for individuals aiming to reduce their fat intake, while ice cream can contain 10% to 25% milk fat. Some frozen yogurt brands also include probiotics, which support gut health, a benefit that traditional ice cream lacks.
If you're lactose intolerant, frozen yogurt may aid in digestion due to its lower lactose content, making it a suitable alternative.
Both frozen yogurt and ice cream provide calcium, essential for bone health, but frozen yogurt might offer additional vitamins and minerals depending on its ingredients.
To summarize, while both treats have their perks, frozen yogurt tends to present more health benefits overall.
Flavor and Texture Differences

The flavor and texture of frozen yogurt and ice cream create distinct experiences for your taste buds. Frozen yogurt usually has a tangy flavor profile thanks to the cultured milk it contains, while ice cream tends to be sweeter and richer due to its higher milk fat content, which is at least 10%.
This difference in milk fat affects the creamy texture of each dessert; frozen yogurt typically ranges from 2-6% milk fat, giving it a lighter, smoother mouthfeel. Many vegans enjoy exploring vegan alternatives to traditional dairy desserts, which can include plant-based frozen yogurts.
Ice cream's denser texture results from its fluffiness, which comes from incorporating air during production. Although soft-serve versions of both are smoother, ice cream remains denser overall.
When you indulge in frozen yogurt, you might notice that its flavor balance can lead to higher sugar content, counteracting its natural tanginess. This can influence your preference between the two options.
For a creamier experience, ice cream is often the go-to, while frozen yogurt provides a revitalizing, slightly tangy alternative. Each dessert offers unique characteristics, allowing you to choose based on your cravings and taste preferences.
Portion Control and Serving Sizes

Maintaining portion control is fundamental when enjoying frozen yogurt and ice cream, especially given their calorie and sugar content. A typical serving size of 1/2 cup can contain significant calories and added sugars, making it imperative to monitor what you consume.
Many self-serve frozen yogurt shops encourage larger portions, leading to increased calorie intake if you're not careful. Ice cream, with its richer flavor and creamier texture, can also tempt you to exceed the recommended serving size. The toppings you choose can further amplify the calorie and sugar content of both treats, so limiting them is essential for better portion control.
To help you navigate portion sizes, here's a quick reference table:
| Treat | Typical Serving Size | Calories (Approx.) | Added Sugars (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frozen Yogurt | 1/2 cup | 100-150 | 10-20 |
| Ice Cream | 1/2 cup | 200-300 | 15-30 |
| Toppings (1 oz) | 1 oz | 50-100 | 5-15 |
Practicing mindful eating can help you enjoy smaller portions while being aware of your overall calorie intake.
Probiotics and Digestive Health

When you consider the health benefits of frozen yogurt compared to ice cream, probiotics play a key role in its appeal. These beneficial bacteria can markedly enhance your gut health and improve digestion. Many frozen yogurt brands include probiotics, which are essential for maintaining a balanced gut microbiota. This balance may help reduce gastrointestinal issues like bloating and constipation.
However, not all frozen yogurt contains live cultures, so you should look for products that display the National Yogurt Association's seal to verify you're getting these health benefits. The fermentation process used in making frozen yogurt is designed to boost probiotic content, although keep in mind that freezing may kill off some of these beneficial bacteria.
Regularly consuming probiotics from frozen yogurt can support your immune function and contribute to overall digestive health. Incorporating this tasty treat into your diet can help you enjoy both flavor and health benefits.
Customizing Your Dessert

When you're customizing your dessert, think about how you can enhance both flavor and nutrition.
You can choose from a variety of healthy toppings like fresh fruit or nuts, which not only add taste but also boost the nutritional value.
Flavor Profile Variations
Frozen yogurt offers a unique canvas for dessert customization, allowing you to tailor your treat to match your taste preferences. Its flavor profile is distinct, thanks to the use of cultured milk, which gives it a tangier flavor compared to the sweeter, creamier taste of ice cream. If you prefer lighter options, frozen yogurt's fruit-based or tart flavors are perfect for your palate.
You can easily customize your frozen yogurt by adding toppings like fresh fruit, nuts, or granola. These additions not only enhance the flavor but also boost nutritional value.
In contrast, ice cream typically focuses on richness and indulgence, with flavors like chocolate fudge or cookie dough that highlight its higher fat content.
However, be mindful of the sugar content in frozen yogurt. Sometimes, the tanginess is balanced with higher sugar levels, which may surprise you.
Depending on the frozen yogurt's production method, the texture can vary, offering options from smooth, soft-serve to firmer varieties. Each choice affects your overall dessert experience, making it essential to reflect on how you want to customize your treat.
Healthy Topping Options
Customizing your frozen yogurt with healthy toppings can elevate your dessert while keeping it nutritious. Start by adding fresh fruits like berries, bananas, or mangoes. These fruits provide natural sweetness and essential vitamins without excessive sugar.
Next, consider incorporating nuts and seeds, such as pistachios or chia seeds. They offer healthy fats, protein, and fiber, enhancing the nutritional profile of your treat.
For a touch of indulgence, opt for dark chocolate chips instead of milk chocolate. This choice reduces sugar intake while adding antioxidants and a rich flavor. You can also drizzle Greek yogurt or nut butter over the top. These toppings introduce extra protein and probiotics, contributing to gut health and keeping you feeling full longer.
Be mindful to avoid sugary syrups and excessive candies, as they can greatly increase calories and sugar content, undermining the health benefits of your frozen yogurt.
Homemade Alternatives

Making your own frozen yogurt at home can be a healthier and more enjoyable option than buying it from the store. By using Greek yogurt, you boost protein content and reduce calories, making your homemade frozen yogurt a nutritious dessert.
Blending your favorite fruits with yogurt and freezing the mixture allows you to create a delicious treat with lower added sugars, tailored to your taste preferences. You can control your sugar intake by using natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup, unlike many commercial options that are packed with high added sugars.
Plus, making frozen yogurt at home gives you the flexibility to adjust the ingredients for any dietary restrictions. You can easily incorporate healthy toppings like nuts, seeds, or fresh fruit to enhance both flavor and nutritional benefits.
Not only is this method a cost-effective way to enjoy frozen yogurt, but it also empowers you to create a tailored recipe that fits your lifestyle. In no time, you can whip up a delightful dessert that satisfies your cravings while keeping your health goals in check.
Consumer Tips for Choices

When you're choosing between frozen yogurt and ice cream, always check the nutritional labels to see what's really in each option.
Keep an eye on portion sizes, especially at self-serve stations, to avoid going overboard on calories and sugars.
Nutritional Label Insights
Guiding through the nutritional labels on frozen yogurt and ice cream can help you make more informed choices. When you're checking the calories, you'll find that frozen yogurt typically averages around 114 calories per half-cup serving, while ice cream usually has about 140 calories. This lower calorie count can be appealing if you're watching your intake.
Next, pay attention to the fat content. Frozen yogurt contains about 3%-6% milk fat, whereas ice cream must have at least 10% milk fat by law.
However, be cautious—frozen yogurt can sometimes have higher added sugar levels than ice cream. Always check the nutritional label for total sugar content to avoid surprises.
Both options offer similar calcium levels, with frozen yogurt providing approximately 143mg and ice cream around 128mg per 100g, which is beneficial for bone health.
If you're interested in probiotic benefits, look for labels indicating "live and active cultures" on frozen yogurt. Not all brands include these beneficial bacteria, so this detail can make a significant difference in your choice.
Portion Control Strategies
Controlling your portions of frozen yogurt or ice cream can make a big difference in your overall calorie intake. Aim for a portion size of half a cup to manage those calories, as both treats can be calorie-dense.
When you're at a self-serve station, be mindful of your toppings; they can greatly increase both sugar and calorie content. Opt for fresh fruit or nuts instead of sugary options like candy or syrups for a healthier choice.
Reading nutritional labels is essential. Check for added sugars and select options with lower sugar content to make better decisions.
If you're craving something sweet, consider sharing a dessert with a friend or family member. This way, you can reduce portion sizes while still enjoying the treat together.
Lastly, practice mindful eating. Savor each bite and pay attention to your hunger cues. This approach can help prevent overeating during dessert time, allowing you to enjoy your frozen yogurt or ice cream while keeping your calorie intake in check.
Balancing Treats in Your Diet

Treats can definitely have a place in your diet, and finding the right balance is important for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Both frozen yogurt and ice cream can be enjoyed in moderation, but it's imperative to pay attention to calories and fat content. Frozen yogurt is often a healthier choice, containing fewer calories and less fat than ice cream.
When indulging in these treats, portion control is essential. Toppings like candies and syrups can quickly escalate the sugar and calorie count, so choose wisely. Enjoying frozen yogurt or ice cream occasionally promotes a healthier relationship with food. Instead of daily habits, consider them as treats to savor.
Here's a quick comparison to help you make informed choices:
| Frozen Yogurt | Ice Cream | |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | Fewer | More |
| Fat | Less | Higher |
| Toppings | Choose wisely | Be cautious |
| Moderation | Important | Key |
| Nutrition Labels | Check | Significant |
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Frozen Yogurt Better Than Ice Cream for You?
When considering if frozen yogurt's better for you, it often has lower fat and calories. However, watch for added sugars. Always check labels to make informed choices that align with your health goals.
Is Frozen Yogurt Healthy for Weight Loss?
Frozen yogurt can be healthy for weight loss if you watch your portions and choose options with lower added sugars. Keep an eye on toppings, and you'll make a smarter choice for your goals.
Is There Such Thing as Healthy Frozen Yogurt?
Did you know that some frozen yogurts contain probiotics, which might support your digestive health? While not all frozen yogurts are healthy, checking nutrition labels can help you make better choices about sugar and calories.
What Is the Healthiest Ice Cream?
When you're choosing the healthiest ice cream, look for options with lower sugar, natural ingredients, and added nutrients. Check labels for calorie counts and portion sizes to enjoy a treat without compromising your health goals.
Conclusion
In the sweet dance of dessert choices, frozen yogurt often twirls gracefully ahead of ice cream, symbolizing a lighter indulgence. While it may seem like a guilt-free option, remember that both treats can fit into your life's tapestry. Embrace the joy of customizing your dessert, savoring each bite, and balancing these delights with mindful choices. Ultimately, it's not just about health, but the happiness these treats bring to your moments. Enjoy them as part of your delicious journey!
Giulia is the creative force behind our content strategy. With a knack for storytelling and a deep understanding of what our readers want, she plans and develops the content that keeps “Icecream Hater” fresh and exciting. Giulia works closely with the editorial team to ensure that every article, recipe, and review aligns with our mission and vision. She aims to inspire our readers to explore, create, and enjoy ice cream in new and innovative ways.
-

 Vetted3 months ago
Vetted3 months agoWhat Is Dairy Queen Ice Cream Made Of?
-

 Vetted3 months ago
Vetted3 months agoHow Big Is a Pint of Ice Cream?
-

 Ice Cream & Health3 months ago
Ice Cream & Health3 months agoMcDonald’s Ice Cream Cone Prices Unveiled!
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months agoWhat Is the Most Popular Ice Cream Flavor?
-

 Vetted3 months ago
Vetted3 months agoWhat Ice Cream Flavor Am I?
-

 Vetted3 months ago
Vetted3 months agoAre Drumsticks Ice Cream?
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months agoHow Much Is a Pint of Ice Cream?
-

 Vetted3 months ago
Vetted3 months agoWhat Is Gelato Ice Cream?


























